A branch of cyber security called “cloud security” is devoted to protecting cloud computing infrastructure. This includes maintaining data security and privacy across web-based platforms, infrastructure, and apps. Cloud service providers and users, whether individuals, small- to medium-sized businesses, or enterprises, must work together to secure these systems.
On their servers, cloud providers offer services via continuously active internet connections. Since the company depends on consumer confidence, client data is kept confidential and securely maintained using cloud security techniques. However, the client is also partially responsible for cloud security. A successful cloud security solution depends on having a solid understanding of both aspects.
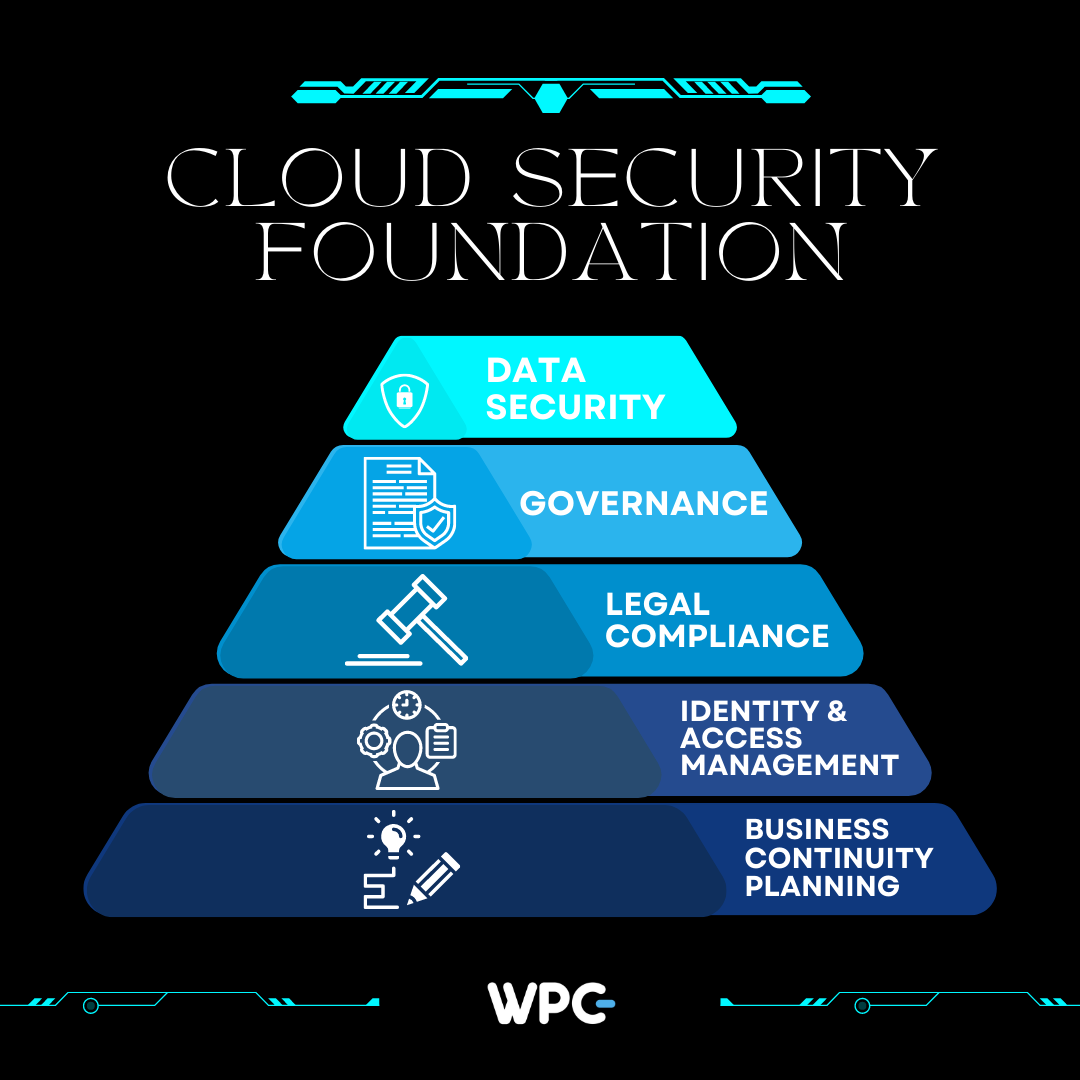
The following categories make up the foundation of cloud security:
- Data security
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Governance (policies on threat prevention, detection, and mitigation)
- Data retention (DR) and business continuity (BC) planning
- Legal compliance
While cloud security may at first glance resemble conventional IT security, this framework actually calls for a different strategy. Let’s take a closer look at cloud security.
What is Cloud Security?
The technologies, procedures, and best practices that safeguard cloud computing environments, cloud-based applications, and cloud-stored data collectively constitute cloud security. Understanding precisely what has to be secured and the system components that must be handled is the first step in securing cloud services.
As an overview, cloud service providers are mostly responsible for backend development against security risks. Clients should concentrate primarily on correct service configuration and secure use behaviors in addition to selecting a security-conscious supplier. Clients should also confirm that any end-user networks and devices are appropriately secured.
Regardless of your duties, the complete scope of cloud security is intended to safeguard the following:
- Physical networks — electrical power, routers, climate controls, cabling, etc.
- Data storage — hard drives, etc.
- Data servers — core network computing hardware and software
- Computer virtualization frameworks — host machines, virtual machine software, and guest machines
- Operating systems (OS) — software that houses
- Middleware — application programming interface (API) management,
- Runtime environments — execution and upkeep of a running program
- Data — all the information modified, stored, and accessed
- Applications — traditional software services (tax software, email, productivity suites, etc.)
- End-user hardware — computers, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, mobile devices, etc.
How Does Cloud Security Work?
Every step taken to secure the cloud aims to achieve one or more of the following:
- In the event of data loss, allow for data recovery.
- Defend networks and storage against nefarious data theft.
- Prevent carelessness or human error that results in data leaks
- Minimize the effects of any system or data compromise
Data Security is a component of cloud security that includes the technological side of threat prevention. Providers and clients can erect barriers to prevent sensitive data from being accessed or seen using tools and technology. Among the most effective tools of those is encryption. Your data is encrypted so that only a person with the encryption key can decode it. Your data will be practically illegible and useless if it is lost or stolen. In cloud networks, emphasis is also placed on security measures for data transit, such as virtual private networks (VPNs).
Identity and access management (IAM) relates to the access rights provided to user accounts. Managing user account authorisation and authentication also applies here. Access controls play a crucial role in preventing users, both good and bad, from accessing and compromising critical data and systems. IAM encompasses techniques like password management and multi-factor authentication, among others.
Governance is concerned with policies aimed at preventing, detecting, and mitigating threats. Threat intelligence, for SMBs and organizations, may assist with tracking and analyzing threats to keep critical systems carefully secured. However, emphasizing safe user behavior standards and training could be advantageous for even individual cloud clients. These are particularly relevant in work situations, but all users can benefit from knowing the safe use guidelines and how to handle hazards.
Data retention (DR) and business continuity (BC) planning include technological disaster recovery methods in the event of data loss. Any DR and BC plan must include techniques for data redundancy, such as backups. Having technical systems in place to guarantee continuous operations might also be beneficial. For a complete BC plan, frameworks for validating backups and proper staff recovery guidelines are just as important.
Legal compliance is concerned with maintaining user privacy as defined by legislative entities. The significance of preventing the commercial exploitation of private user information has been recognized by governments. Organizations must therefore adhere to rules in order to uphold these policies. Data masking is one strategy that hides identity within data through encryption techniques.
Why Do Companies Need Cloud Data Protection
Massive volumes of data are being gathered by businesses, ranging from basically inconsequential information to highly private commercial, financial, and consumer data. Additionally, they are keeping their data in more public, private, and hybrid clouds, cloud storage environments, software-as-a-service applications, and other places than ever before.
Companies are learning how challenging it can be to secure and protect all of their data across various environments as they go along. For instance:
- All of their data and apps are now lost to them.
- Companies no longer have control over who is accessing and utilizing their apps and data, which gadgets are being used for connection, or how their data is possibly being used or shared because the majority of their applications and information are hosted on third-party infrastructure.
- They are unaware of how their data is being stored and protected by cloud service providers.
- While most cloud providers have cutting-edge security, this security has some limitations. After all, cloud security is a shared responsibility between businesses and cloud providers.
- Because various cloud providers have different capacities, cloud data security, and protection may vary.
Additionally, businesses confront a variety of security difficulties, including the possibility for
- Breaches in security
- Stolen or lost sensitive data
- Malware propagation and application flaws
How To Secure The Cloud
Thankfully, there are many things you can take to safeguard your own data stored in the cloud. Let’s look at a few of the common techniques.
One of the finest strategies to protect your cloud-based computing systems is encryption. There are numerous ways to use encryption, and they might be provided by a cloud provider or by a different company that offers cloud security solutions:
- Encryption of all communications with the cloud.
- Encryption of very private data, such as login passwords.
- Encryption from beginning to end for all data transferred to the cloud.
Data in the cloud is more susceptible to interception when it is in motion. It becomes susceptible when it is transferred to your on-site app or when it is migrating from one storage location to another. End-to-end encryption is the greatest cloud security option for sensitive data as a result. End-to-end encryption ensures that no part of your communication is accessible to third parties without the encryption key.
Either you encrypt your data before uploading it to the cloud yourself, or you utilize a cloud provider who will do so for you as part of their service. End-to-end encryption may be excessive if all you plan to store in the cloud is non-sensitive data like films or corporate images. On the other hand, it is essential for information that is financial, private, or commercially sensitive.
If you use encryption, keep in mind how important it is to manage your encryption keys safely and securely. Keep a backup of your keys, but ideally don’t save them in the cloud. Additionally, you might want to routinely update your encryption keys to ensure that anyone who obtains them is kept out of the system whenever you make the switch.
One more effective technique for cloud security is configuration. Basic flaws like incorrect configuration lead to a lot of cloud data breaches. You greatly reduce your danger to the security of the cloud by avoiding them. You might want to think about working with a different cloud security solutions provider if you don’t feel comfortable handling this on your own.
Here are some guidelines you can adhere to:
- Never stick with the default settings. A hacker gains front-door access by using the default settings. Stop doing this to make it more difficult for hackers to access your machine.
- Never leave a bucket of cloud storage open. Hackers might be able to view the content of an open bucket by just visiting the storage bucket’s URL.
- Use security protections that you can activate if the cloud provider provides them. You run the chance of injury if the wrong security options are chosen.
TIPS For Cloud Security
Any cloud installation should also include fundamental cyber security guidelines. Standard cyber security precautions shouldn’t be disregarded, even if you use the cloud. Therefore, if you wish to be as safe as possible online, you should take into account the following:
- Create secure passwords. A password that combines letters, numbers, and unusual characters will be more difficult to decipher. Avoid making apparent decisions, such as substituting an S with the symbol $. Your string creation should be as random as possible.
- Make use of a password manager. You won’t have to keep track of all the passwords you assign to the many services, databases, and applications you use. But you need to make sure your primary password for your password manager is secure.
- Protect the gadgets you use to access your cloud data. If your data is synced across many different devices, any one of them can be a weak point, endangering the integrity of your entire digital footprint.
- Regularly back up your data so that you can fully restore it in the event of a cloud outage or loss of data at your cloud provider. If you are convinced that the different cloud providers do not share infrastructure, you can perform the backup on your personal computer, an external storage drive, or even from one cloud provider to another.
- Change the permissions to prevent anyone or any device from accessing all of your data unless it is absolutely essential. Businesses might accomplish this via database permission settings, for instance. Use guest networks if you have a home network to connect your TV, IoT gadgets, and children. You should only use your “access all areas” pass for yourself.
- Use antivirus and anti-malware software to safeguard yourself. If malware gains access to your system, hackers can quickly access your account.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi to access your data, especially if it does not use robust authentication. To secure your cloud gateway, employ a virtual private network (VPN).
Verify The Security Of Your Cloud Provider
When selecting a cloud security service, security must be one of your top priorities. Because cloud security providers must contribute to the development of a secure cloud environment and share responsibility for data protection, your cyber security is no longer only your duty.
Unfortunately, cloud service providers won’t share the details of their network security with you. This would be the equivalent of a bank giving you information about its safety and its combination numbers.
However, knowing the correct answers to a few straightforward questions will increase your sense of security regarding the security of your cloud assets. You will also be more conscious of whether your supplier has adequately handled the obvious concerns to cloud security. We advise enquiring about the following issues with your cloud service provider:
- Security audits: “Do you often have outside parties examine your security? ”
- Data segmentations: “Is consumer data maintained separately and rationally segmented?
- Encryption: “Does our data have encryption? How much of it is encrypted?”
- Customer data retention: “What customer data retention guidelines are in place?”
- User data retention: “Will my data be appropriately removed if I stop using your cloud service?”
- Access management: “How are access permissions managed?”
Solutions for Enterprise Cloud Security
Over 90% of larger businesses today employ cloud computing, so cloud security is an essential part of a company’s cyber security. For enterprise-level enterprises, private cloud services as well as other expensive infrastructure may be practical. You will still need to make sure that your internal IT is keeping your networks’ complete surface area maintained, though.
If you invest in your infrastructure, cloud security for large company use can be much more adaptable.
Here are a few essential points to remember:
- Manage your accounts and services actively: If you stop using a service or piece of software, make sure to properly shut it off. Old, inactive accounts can be used by hackers to quickly access a cloud network’s complete infrastructure thanks to unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): This can be a password and a different code that is transmitted to your mobile device, or it can be biometric information like your fingerprints. Although time-consuming, it is beneficial for your most private data.
- Analyze the costs and advantages of hybrid cloud: In enterprise use, where you will be managing considerably greater amounts of data, sectioning your data is much more crucial. Whether it is logically separated for separate storage or is individually encrypted, you must ensure that your data is distinct from that of other customers. This is where hybrid cloud services can be useful.
- Be aware of shadow IT: It’s crucial to train your staff to refrain from using illegal cloud services on your systems or for business-related tasks. Your company may be vulnerable to malevolent actors or legal problems if critical data is transmitted through unsafe networks.
End Game
Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that your networks and devices are as safe as possible, regardless of whether you’re an individual user, SMB user, and even a large enterprise cloud user. This begins with each user having a solid awareness of fundamental cyber security. You should also make sure that your networks and all gadgets are secured by a security protection solution that is designed for the cloud.