Endpoint security is the practice of securing every component of an organization that has the potential to get internal access to assets like servers or databases. Because it is such a wide subject, cybersecurity experts are forced to consider every access point a hacker might use to launch an assault.
When hackers plan to attack a company, they first decide which type of mechanism they would try to exploit. This could be a networked device, a website, or a piece of software. Then, while attempting to avoid detection by defense mechanisms, they set about looking for means to carry out their plan.
In this blog, we’ll examine what endpoint security entails in the real world and how businesses may integrate it into their IT security plans to help maintain the appropriate level of workplace cybersecurity.
What Qualifies as an Endpoint?
Endpoint security is a process that makes IT teams examine every access point that third parties could have to their internal network. Each new piece of technology used by employees, such as tablets and smartphones, adds a new vulnerability to be aware of.
Why Endpoint Security is Important
There are various benefits of using an endpoint protection technology that is essential for maintaining business continuity. The following are some ways that endpoint protection might help businesses:
Integrated security management: Modern endpoint protection solutions do away with the previous, fragmented security systems where endpoints are handled independently. The old procedure not only took a lot of time but also left big security holes that were hard to find. IT teams may control hundreds of endpoints from a single interface thanks to contemporary endpoint security software. Security flaws can be quickly found and fixed with a better understanding of the endpoints and network diagram.
Attack vector protection: Cybercriminals use a range of attack vectors to insert malicious payloads into the systems of their victims. Attack vectors include things like compromised passwords, phishing emails, and insufficient or absent encryption. Numerous attack paths can be found and stopped with an endpoint protection program.
Efficient security operation: Endpoint protection systems provide the ability to automate a range of security operations without the need for human involvement. Through the use of endpoint protection solutions, technicians may quickly manage, register, update, and remove hundreds of endpoints. This not only increases the overall success rate and efficiency of the security process but also allows IT specialists to concentrate on high-value, mission-critical jobs.
Improved business resiliency: Businesses need to adopt strict security measures if they want to remain competitive, especially as workforces become more distributed, workplaces become more diverse, and cybercrime is rising at an unprecedented rate. Cyberattacks cannot be prevented. Digital forensics incident management capabilities and the appropriate endpoint protection tools can both help you quickly recover any damaged data.
Business reputation protection: The Ponemon Institute estimates that a data breach costs $3.92 million on average. However, the harm a breach may do to your company or reputation is much larger. 60% of businesses fail or go out of business after a data breach.
Customers and clients prefer to work with businesses that have strong security measures in place and adhere to cybersecurity regulations in the present economic climate. The use of an endpoint protection tool is now required and cannot be avoided.
How Does Endpoint Protection Work?
Endpoint security is the process of protecting the information and processes related to the specific devices connected to your network. Platforms for endpoint protection (EPP) look at files when they connect to the network to function. Modern EPPs use the cloud to store a constantly expanding database of threat data, relieving endpoints of the bloat caused by having to store this data locally and the upkeep needed to keep these databases current. Increased speed and scalability are also made possible by accessing this data on the cloud. System administrators are given access to a centralized panel by the EPP, which is deployed on a network gateway and enables cybersecurity experts to remotely manage security for each device.
After that, the client software is assigned to each endpoint. It can either be installed locally on the device or given as a SaaS and maintained remotely. After the endpoint is configured, the client software can remotely manage corporate rules, verify log-in attempts out of each device, and send updates to the endpoints as needed. Application control, which prevents the use of illegal or risky programs, and encryption, which lessens the risk of data loss, are two methods through which EPPs safeguard endpoints. The EPP can swiftly identify malware and other dangers once it is configured.
Endpoint Protection Platforms vs. Traditional Antivirus
Traditional antivirus solutions and endpoint protection platforms (EPP) differ in several important aspects.
Endpoint Security vs. Network Security: Antivirus software is made to protect a single endpoint by providing visibility into and, frequently, access to only that endpoint. However, endpoint security software takes a holistic approach to the enterprise network and can provide visibility of every connected endpoint from a single point.
Management: Earlier versions of antivirus software required users to manually maintain the databases or permit updates at predetermined times. EPPs provide interconnected security that transfers management duties to business IT or cybersecurity teams.
Protection: Traditional antivirus programs searched for viruses using signature-based detection. This implied that you might still be in danger if your users hadn’t recently updated their antivirus software. Modern EPP systems are automatically updated by utilizing the cloud. Additionally, by observing suspicious activity, tools like behavioral analysis can be used to detect previously unknown risks.
Choosing the Best Endpoint Security for Your Company
Ideally, the majority of firms already have a foundational level of IT security safeguards in place. As a result, when considering endpoint security, they must choose between giving up on their present toolkit and investing in a new suite and trying to add on specific components to properly satisfy their demands.
Cost plays a big role in choosing an endpoint security program. The cost of a vendor will normally fluctuate based on the number of users your business has and the size of the network you are running. Remember that various security protocols or rules may be required of you based on the sector or industry in which your business operates.
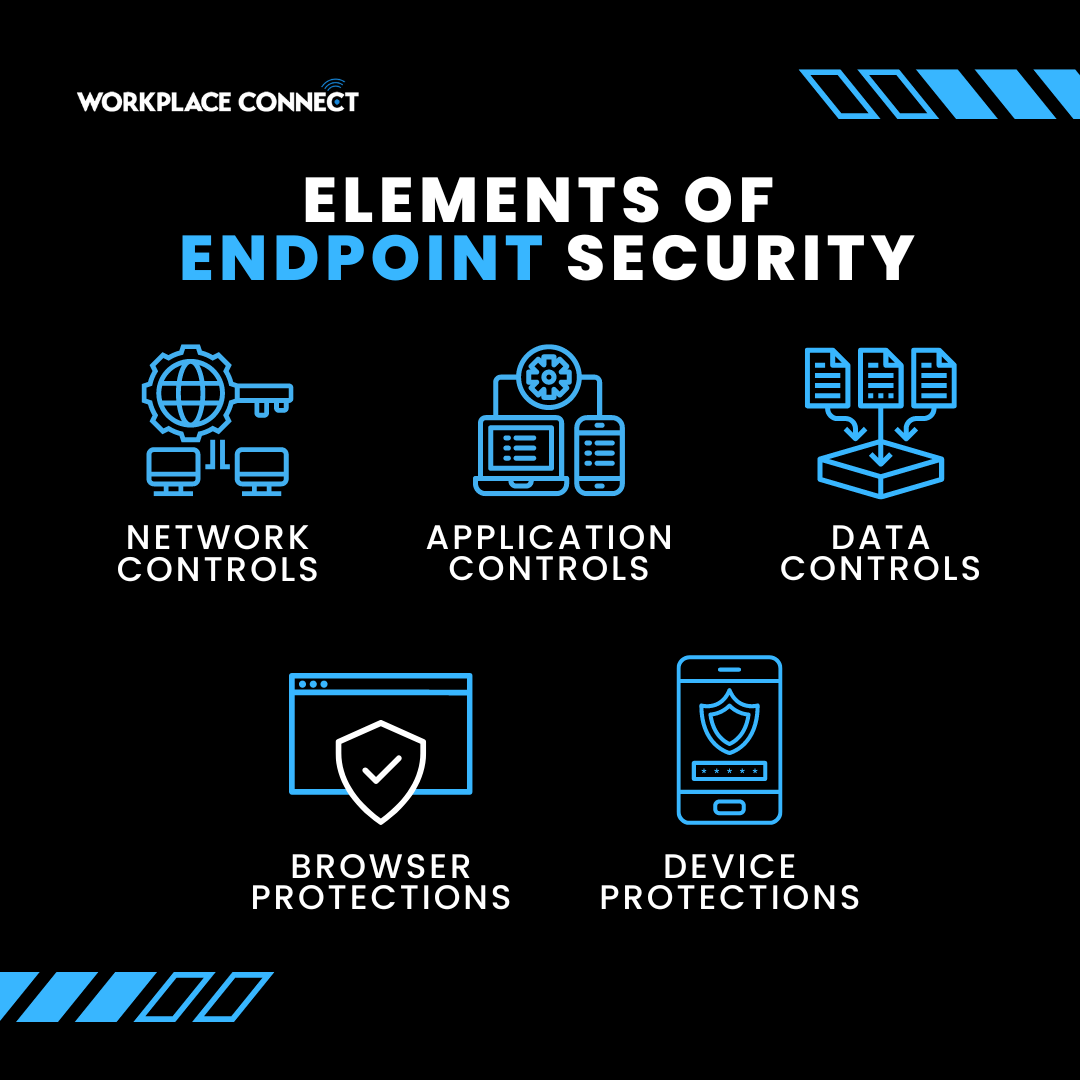
Essential Endpoint Security Elements
You must pay special attention to the specific benefits you will receive for your investment when you compare endpoint solutions. While some suppliers may advertise a full suite, they can be missing some features that other options offer. These are the key components to watch for:
- Device Protection – How is mobile endpoint security implemented? To defend against assaults like ransomware, your solution should contain antivirus and malware protection for PCs as well as mobile devices such as phones and tablets.
- Network Controls – A comprehensive firewall should be able to filter all incoming traffic through the endpoint security system and spot any potential threats.
- Application Controls – Integration with application servers is required for this to keep track of and restrict endpoint access.
- Data Controls – Tools that assist in preventing data leaks and enhancing data security through the encryption of sensitive data are included in this.
- Browser Protections – A web filter option is frequently present in endpoint security systems, allowing you to choose the kinds of websites that your users are permitted to browse while connected to a network.
Is Endpoint Security Sufficient on its Own?
Many businesses believe that having an endpoint protection system is enough. In actuality, this approach only addresses one component of your security configuration. To provide total security, a business must additionally use several different security tools, solutions, and procedures. A business needs data backup and recovery solutions, anti-phishing email scanning software, and even cybersecurity training to reduce hazards that can occasionally result from employee negligence.
Here are some actions you may take to guarantee the security of your IT infrastructure:
- Execute routine IT evaluations
- Regularly develop, implement, and update security policies.
- Implement a rigid password policy.
- Implement strict guidelines for data backup
- Establish a thorough BYOD policy.
- Continue to update your systems.
- Use a strong email security program.